
How do I style a template in Vue?
How can I improve the look of my Vue application? In what ways does the style impact the functionality? Isn’t coding a website or application enough; why should the styling matter? These questions often pop up when discussing Vue application styling. Indeed, all of these issues intertwine to create a holistic user experience that extends beyond simple interactions.
A common problem within the Vue developer community is the correct and efficient way to style a Vue template. According to a Stack Overflow Developer Survey and the recent trends cited by Toptal, many developers often express difficulties in styling, leading to applications that do not meet the desired user experience standards. Therefore, it is imperative to identify solutions that can guide Vue developers on how to correctly style their templates, which includes integrating designs that amplify the user interaction while ensuring the functionality is not compromised. Reports such as the State of CSS survey also confirm that there is a strong need for tutorials and guides on Vue styling in the US market.
In this article, you will learn the essential methods, tips, and tricks for Vue template styling. We delve into the significance of styling in Vue applications, looking at why it is an aspect that can no longer be overlooked due to its impact on the end-user experience. We discuss the effect that poor styling can have on your application’s functionality.
Moreover, we present an in-depth guide on effective Vue template styling, touching upon various styling techniques while highlighting the importance of each. Furthermore, expect a collection of practical examples, expert insights and referenced solutions you can apply in your future Vue projects, contributing to an improved user experience and application functionality.
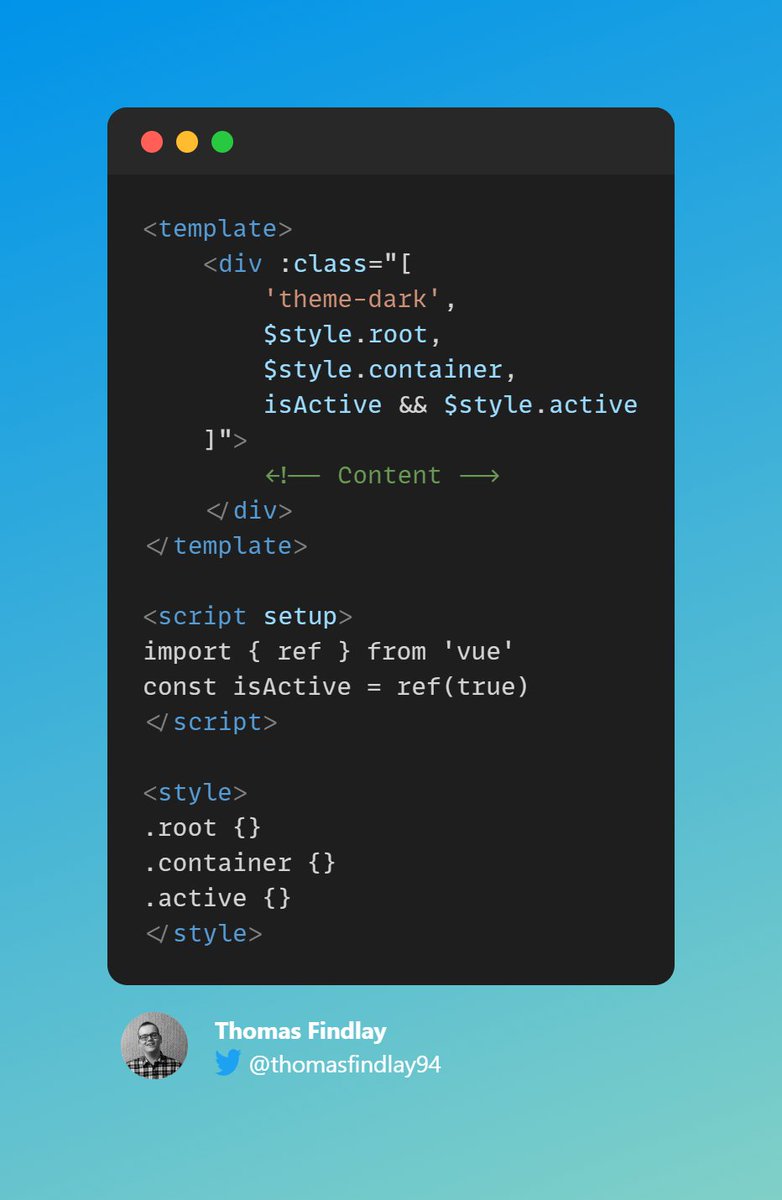
Definitions and Basics of Styling a Template in Vue
Vue.js is a popular JavaScript framework used for building user interfaces. The term ‘template’ in Vue refers to the HTML code which forms the structure of a Vue component. ‘Styling’ means defining the look and feel of the template, such as colors, fonts, and layout.
The design in Vue.js is primarily achieved using CSS (Cascading Style Sheets). CSS is a style sheet language used for describing the look and formatting of a document written in HTML. Styling a template in Vue can be done in multiple ways – either inline, using style tags in the template, or by linking to an external CSS file.
Unleashing Incredible Styles in Vue Templates: Understanding the Essentials
Understanding Vue.js Styling
The topic of Vue.js styling is integral to the overall appeal and functionality of your Vue templates. Even though Vue.js follows a component-based architecture, it is still possible to style individual components and entire templates. The primary way to do this is through CSS, which can be integrated into Vue.js in many ways.
You can use inline styles, where the styling rules are written within the style attribute of the HTML elements. While this method allows you to quickly style elements, it can make your HTML messy and hard to read.
A better alternative, and the more popular approach, is to use CSS classes and ids to style different elements in your Vue templates. With this method, you can write a CSS rule once and apply it to multiple elements at once. The style tag can be used in single-file components, and scoped CSS can limit the effect of styles to the current component only.
Working with Vue.js Styles
CSS is not the only styling option available in Vue.js. There are several other alternatives like CSS Pre-processors (Sass, Less, Stylus), CSS Modules and CSS-in-JS libraries. Vue provides excellent tooling support for these options. Pre-processors extend the CSS syntax to introduce variables, mixins, and other powerful features. CSS Modules are a CSS file in which all class names and animation names are scoped locally by default. CSS-in-JS libraries, such as emotion or styled-components, allow you to write CSS codes right inside the JavaScript files.
- Inline Styles: Quick, but may lead to messy HTML.
- CSS Classes and IDs: A more organised way to style Vue.js templates. Allows for reusable rules.
- CSS Pre-processors: Enhance CSS syntax with variables, mixins, and other features.
- CSS Modules: Locally scoped CSS.
- CSS-in-JS: Write CSS inside your JavaScript files.
To use these styling options in Vue.js, you need to understand their syntax, rules, and the way they interact with Vue.js components. Moreover, you must have a solid working knowledge of Vue.js basics and components. With this knowledge, you can creatively style your Vuejs templates to create visually appealing and user-engaging interfaces.
Remember, styling in Vue.js goes beyond aesthetics; it also contributes to the overall functionality and effectiveness of the application. Hence, learning and leveraging these styling methods is key to creating high-quality, highly-useful Vue.js applications that deliver the best user experience.
Amplify your Vue Template Styles: Striking a Balance Between Function and Aesthetics
Templating Goes Beyond Code Creation
Thought-provoking question: How often do you consider aesthetics in your quest for peak functionality? It’s crucial to remember that, in Vue, the template isn’t simply for structuring your application’s content. It also dramatically influences aesthetics and user experience. For instance, inconsistent or conflicting styling within a Vue template can significantly harm an application’s professionalism and user-friendliness. Fortunately, you can learn how to strike the ultimate balance between form and function in your Vue templates, achieving both functional efficiency and exceptional aesthetic design.
The Shortcomings of Mismanaged Vue Template Styling
Many developers, especially those new to Vue, encounter issues with template styling. One fundamental issue is inconsistent style application, often due to mixing inline styles with external stylesheets. This results in a lack of uniformity across components, creating visual discord and complicating iterative changes. Additionally, many developers neglect to factor in responsiveness when styling their Vue templates. Considering the increasing variety in device screens, templates that don’t adapt to different viewports can deliver unsatisfactory experiences to end-users. Lastly, maintaining readability and efficiency of Vue templates can be challenging when developers overload them with complex styles, leading to unnecessary application bloat or even impacting performance.
Forerunners in Vue Template Styling Strategy
Following the best practices from proficient Vue developers can aid in resolving the aforementioned issues. For instance, using style encapsulation in components is a popular approach among Vue experts. Each component has its unique fashion, leading to a more structured and predictable application look. Another promising approach is embracing Responsive Design. Developers can leverage Vue’s in-built capabilities to detect viewport changes in real-time and adjust the application’s look accordingly for optimal user experience. Finally, emphasizing code readability and maintainability should be at the core of every Vue styling strategy. By organizing styles logically and commenting on code usefully, developers can significantly raise their application’s sustainability while reducing development and maintenance time.
Transforming Vue Templates: An In-depth Exploration into Advanced Styling Techniques
An Intriguing Inquiry: Vue Styling Made Easy?
Is there a way to bring interactive features to your application without improbable amounts of effort? The answer to that concerns the proficiency in manipulating Vue templates. Vue.js, a widely adopted open-source JavaScript framework, has gained immense popularity due to its joint advantage of simplicity and performance. The heart of Vue’s allure lies in its unique ability to directly style templates, which asserts more command over a project, promotes code reusability, and ensures a flawless user interface.
While Vue.js enables engineers to shape captivating user interfaces by using the Vue Component, it introduces both comfort and discord. The question many developers often find themselves asking is: ‘Is Vue.js simplifying or complicating the stylistic process?’. In principle, Vue.js is intended to enhance the styling process, but the manner in which it is utilized greatly determines whether this potential is realized.
Conceptualizing the Prevalent Issue
Styling Vue templates could pose as a demanding task, particularly for newcomers to Vue.js. The main problem arises when developers attempt to modify components’ style while avoiding interference with other components. The recommended method to implement styles in Vue.js is by using scoped CSS. However, many developers inadvertently get into the trap of code redundancy, creating an unnecessary and inconvenient overhead, especially in large-scale projects. They would instead find themselves styling every single component separately, leading to code duplication. Hence, a well-established understanding of how to effectively style Vue templates is indispensable.
Adopting the Effective Methodology
The Vue.js community has persistently come up with solutions that range from utilitarian conventions to powerful pre-compilers allowing developers to avoid the previously mentioned issues and maintain larger Vue applications. For instance, one of the best practices in Vue.js is the use of single file components (SFCs). An SFC includes three parts: template, script, and style. This makes it easier to manage, prevents unintended altering of properties, and keeps the global namespace clean.
Moreover, Vue.js offers you to utilize CSS Modules, a popular system for modularizing and composing CSS. By using CSS Modules, Vue.js developers can write CSS in more maintainable and scalable ways. Therefore, employing CSS Modules for styling Vue.js applications can result in simpler, more robust, and more maintainable styles.
Lastly, you can also leverage pre-processors such as Sass or Less to style your Vue templates. These pre-processors enable more complex styling, and they’re integrated in Vue loader, allowing you to use them freely in your Vue templates. Here, you can harness functions, mixins, and variables to improve reusability of your CSS. With this, your styles become modular and maintainable, reducing overly complex and repetitive CSS.
Conclusion
Isn’t it fascinating how Vue.js has emerged as a potent tool in the realm of web development, allowing for more intuitive and visually pleasing designs? The ability to style your templates in Vue offers a new dimensions of creativity while ensuring your application’s robust functionality. Proper understanding and application of Vue’s styling techniques can significantly improve your application’s user-interface and user-experience.
We encourage you to stay tuned to this blog, as we will continue to delve deeper into these creative opportunities Vue provides. We aim to provide insightful content that will assist you in better understanding the wide array of mechanisms Vue.js offers. It’s an exciting journey, and we’re glad to have you on board with us.
Lastly, we understand you may be eager to further enhance your Vue.js proficiency. That’s why we are excited about our forthcoming posts, designed to equip you with advanced knowledge and help you truly master Vue.js. These upcoming articles will contain in-depth guides and demonstrations that will enrich your current skillset. So, keep visiting our blog and stay ahead in achieving your web development goals.
F.A.Q.
Sure! Here is your FAQ section:
1. How do I integrate CSS styling within my Vue.js template?
You can integrate CSS directly in your Vue.js template by specifying them within the “ tags in your component file. However, you might want to consider using single-file component style for more complex arrangements.
2. Can I use external CSS files in my Vue.js template?
Yes, you can use external CSS files. To do this, you simply need to link the CSS file in the HTML file where your Vue.js app is initiated.
3. How do I use scoped CSS in my Vue.js template?
Scoped CSS can be activated in your Vue.js template by adding the ‘scoped’ attribute to your style tag. This keeps your CSS rules limited to their component and prevents them from leaking out into other components.
4. What is single-file component style in Vue.js?
Single-file component style is a Vue.js-specific style where all the HTML, CSS, and JavaScript code of a component is contained in one `.vue` file. This style can enhance readability and maintainability of your code.
5. Can I use CSS pre-processors in Vue.js templates?
Absolutely! Vue.js supports CSS pre-processors like SASS or LESS. You just need to specify the pre-processor in the style tag’s `lang` attribute. Note that you’ll need to configure your build tools to compile these correctly.

